
Dr. Parveen Kumar, Dr. R. K. Arora, Dr. Pawan Sharma
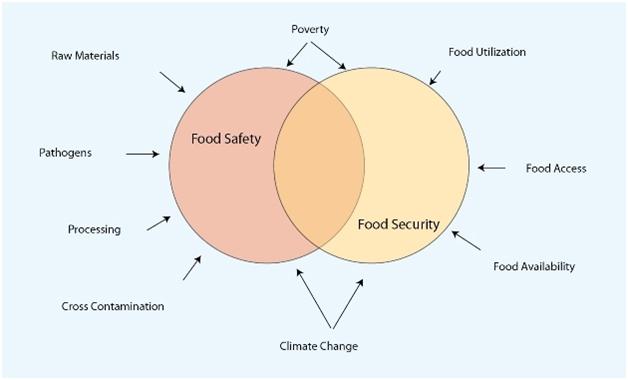
Food safety and food security are very intricately linked with each other having a profound impact on quality of human life. While food security is the adequacy of food to society, the equitable distribution, confirmed supply, fair access and sustained sources; food safety on the other hand encompasses many facets of handling, preparation and storage of food to prevent illness and injury. So, food safety and security refers to access to healthy and sufficient amount of nutritious food that can sustain life and promote good health. Food safety is an umbrella term that encompasses many facets of handling, preparation and storage of food to prevent illness and injury. Access to sufficient amounts of safe and nutritious food is a basic human necessity, required to sustain life and promote good health. Although the food safety and food security are inextricably linked, yet the importance of food safety in this relationship is often overlooked. Improved food safety will contribute to improved nutritional status and the reduction and prevention of non communicable diseases, including cancer.
Food security has been defined by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations (UN) as; ‘Food security exists when all people, at all times, have physical, social and economic access to sufficient, safe and nutritious food which meets their dietary needs and food preferences for an active and healthy life. Household food security is the application of this concept to the family level, with individuals within households as the focus of concern’ (FAO 2003). Despite a record production of food grains there are millions and millions of undernourished peoples across the globe. Most of the undernourished people in the world live in developing countries, 2/3 of them in just seven countries (Bangladesh, China, the Congo, Ethiopia, India, Indonesia and Pakistan) and over 40 percent live in China and India alone. Sub-Saharan Africa has the highest proportion of undernourished with 30% of the population being in this category. Food security is affected by climate change, dependence on fossil fuels, and loss of biodiversity and use of food crops for bio fuels, among many other factors.
There is a critical role of food safety in ensuring food security. Th deep insightful definition of food security by the FAO has been wrongly simplified. Food security has often been conceived merely in terms of having sufficient food. Nutrition and safety, the two critical components of that definition are often afterthoughts, and some instances are simply forgotten. As such, it becomes necessary that all the elements of food security including safety must be addressed simultaneously in order to achieve the goal implicit in the FAO definition. Not giving
proper attention to the food security aspect has only added to the disease burden all across the globe. The World Health Organization states that each year, food borne illnesses cause almost one in 10 people on the planet to fall ill. Some 420,000 deaths a year are believed to result from food borne illnesses, a significant proportion of these in children less than five years old. Similarly contaminated food causes some 230,000 diarrheal deaths a year. The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) report from 2011, which focused on the United States estimated that one in six people in the US is a victim of food borne illness, with 3,000 related deaths each year. If we were to simply extrapolate the CDC data to the globe that would suggest that approximately a billion people suffer from some variety of food borne illness each year. FAO also estimates that 4.5 billion people are exposed to aflatoxin annually, many of them having consumed food considered unfit for onward distribution. The way we look at unsafe food, and at food waste, must change.
Another unfortunate but important aspect of the food production system is that not all the food produced for human consumption is eaten. FAO estimates that around one third of the food produced in the world every year approximately 1.3 billion tons is lost or wasted, with quantitative food losses and waste per year estimated at around 30% for cereals and 40–50% for root crops. These figures do not include the unsafe food that is being consumed. We are probably significantly overestimating the global food supply because the unsafe food is not extracted from the data. The much bigger challenges lies ahead. According to the FAO, ‘Over the next four decades, the world’s population is forecast to increase by 2 billion people and to exceed 9 billion people by 2050. Recent FAO estimates indicate that to meet the projected demand, global agricultural production will have to increase by 60 percent from its 2005–2007 levels. To meet this demand, we will have to optimize food supply systems in an unprecedented way. The world must solve three food issues simultaneously i. e end hunger, double food production by 2050, and do both while drastically reducing agriculture’s impact on the environment. We have to produce as much food in the next 40 years as we have in the last 8,000 and if we want to do it without expanding further into the environment, we’re going to have to produce twice as much food on the same amount of land.
It is clear that we cannot achieve food security unless we tackle food safety on a global scale. To create awareness among the masses regarding the importance of food safety in ensuring food security, world food safety day is celebrated on June 07 every year. This day is celebrated to draw attention and inspire action to help prevent, detect and manage food borne risks, contributing to food security, human health, economic prosperity, agriculture, market access, tourism and sustainable development. It is a day to have action oriented campaign that will promote global food safety awareness and call upon countries and decision makers, the private sector, civil society, UN organizations and the general public to take action. Food safety is a shared responsibility between governments, producers and consumers. Everybody has a role to play from farm to table to ensure the food we consume is safe and will not cause damages to our health. Through this day the World Health Organization as the global health body also pursue its efforts to mainstream food safety in the public agenda and reduce the burden of food borne diseases globally